-
86-13906171096
-
waimao@hanshen.com.cn
-
East No.100,Furong Yilu Road, Xishan Economic Development Zone,Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- Home
- About Us
-
Products
-
Solutions
- Sheet metal processing
- Kitchen and bathroom hardware
- Hardware products
- Door and window guardrails
- Ventilation ducts
- Industrial electrical cabinet
- Auto parts
- Environmental protection equipment
- Automobile manufacturing
- Food equipment
- Advertising Industrial Gifts
- Aluminum veneer industries
- Medical equipment
- New energy
- Rail transit
- Steel structures
- Shipbuilding
- Aerospace
- Metallurgy
- Case
- Videos
- News
- Contact Us
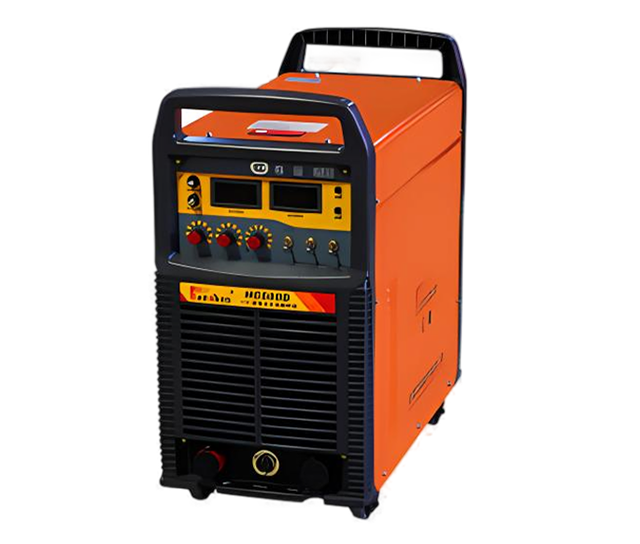
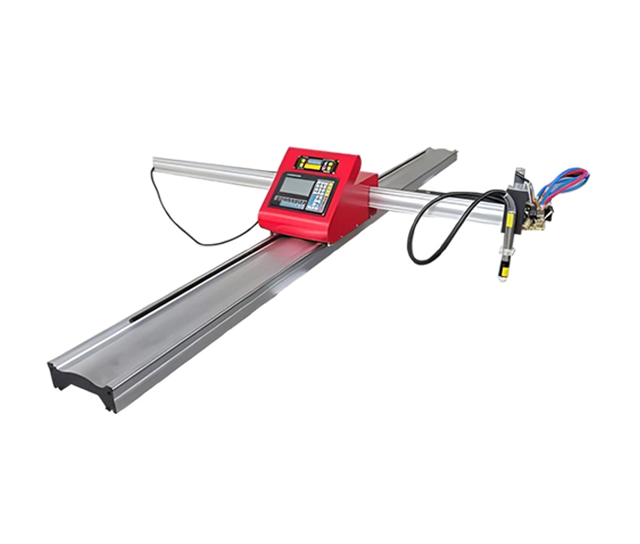
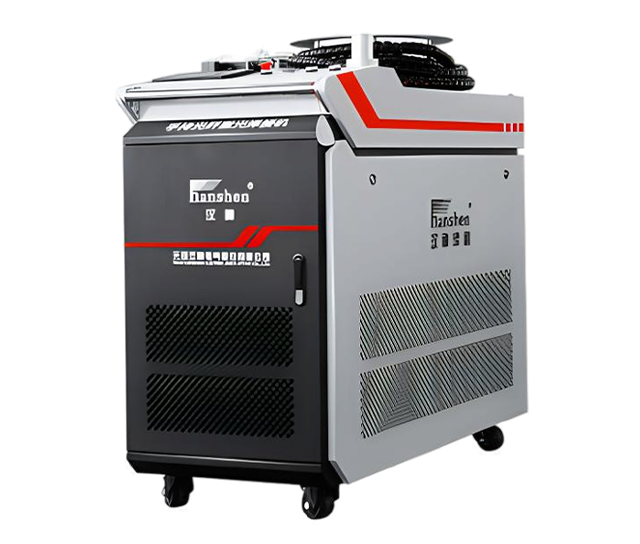
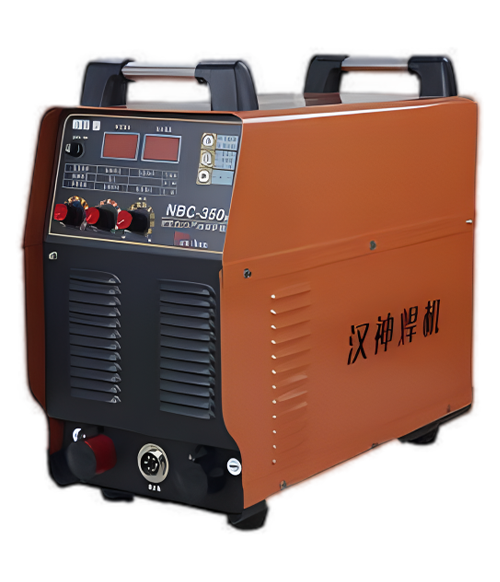
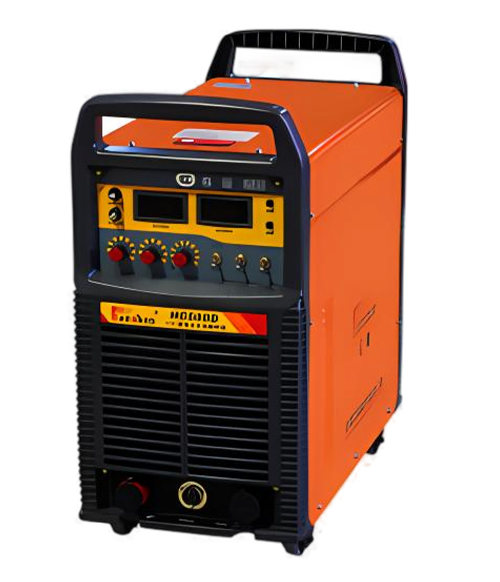
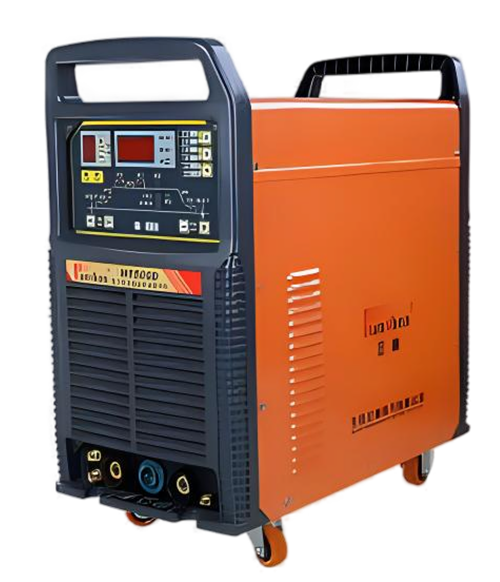
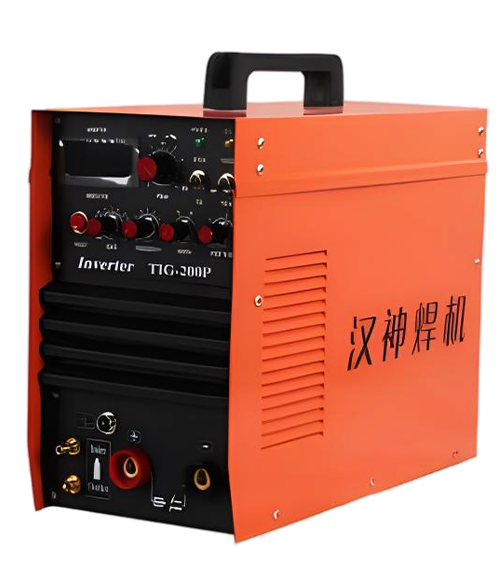
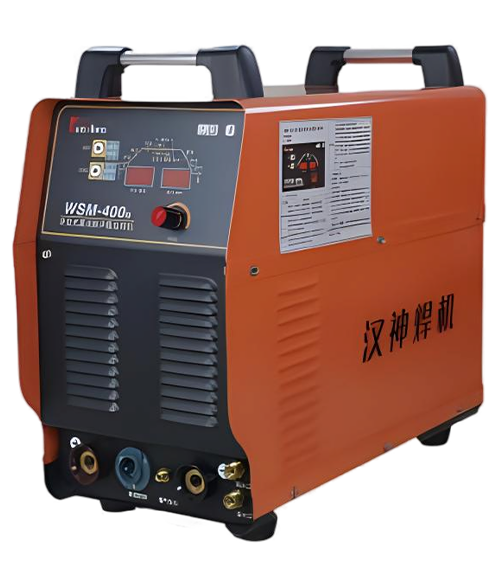
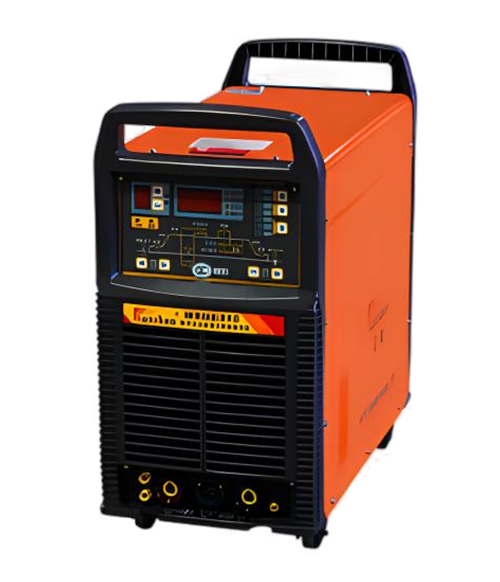
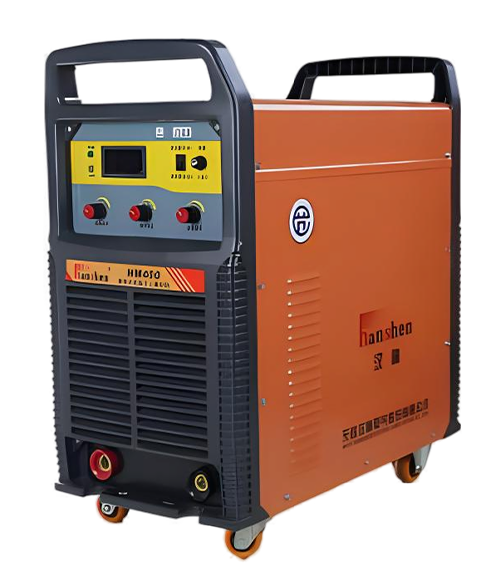
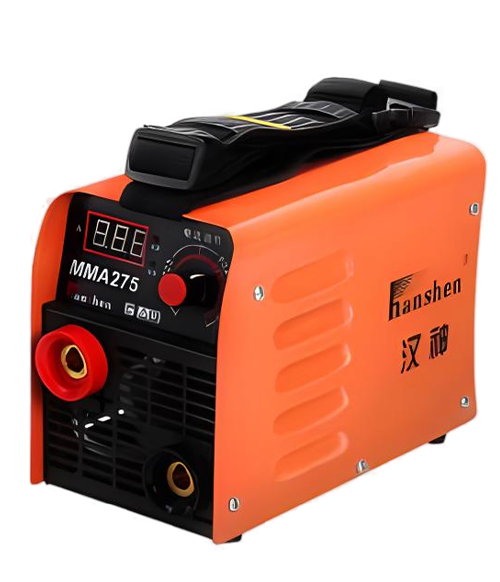
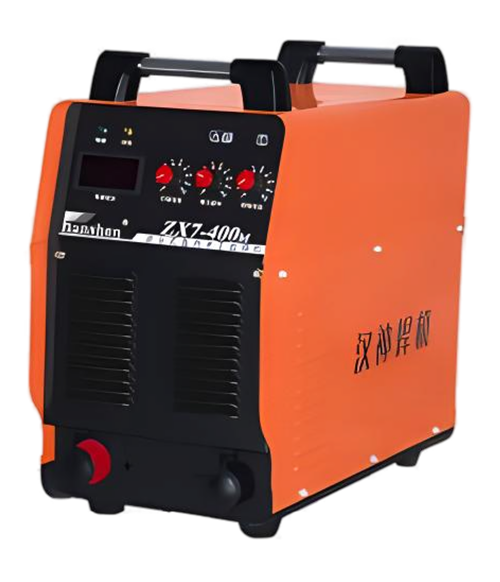
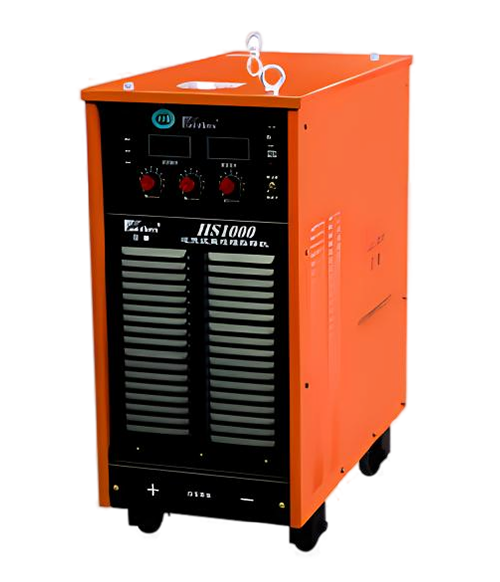
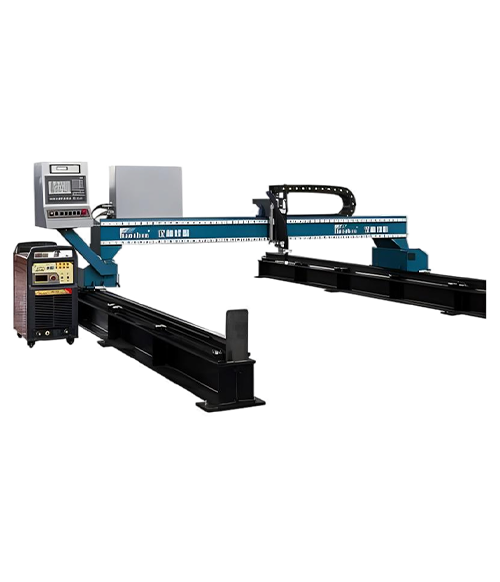
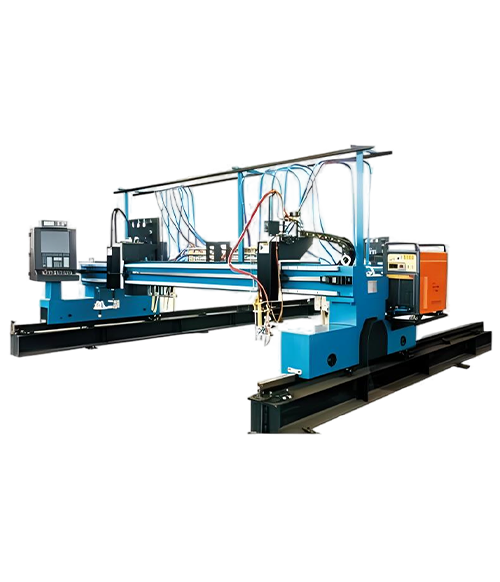
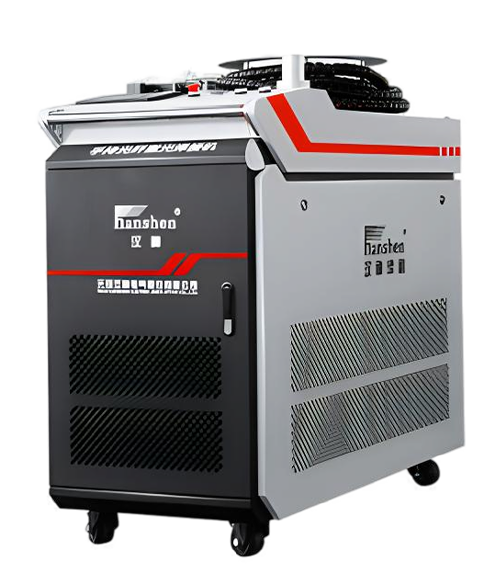
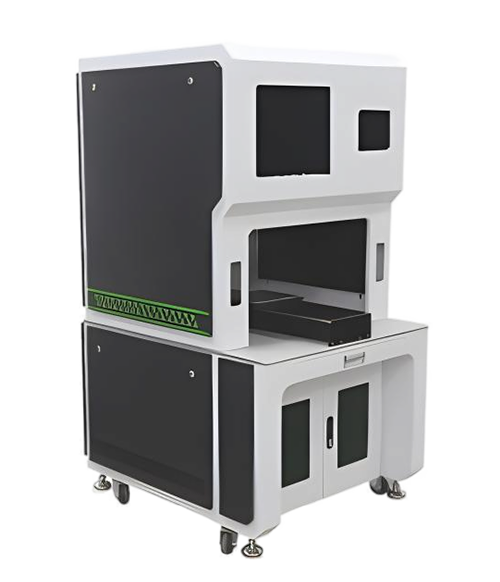
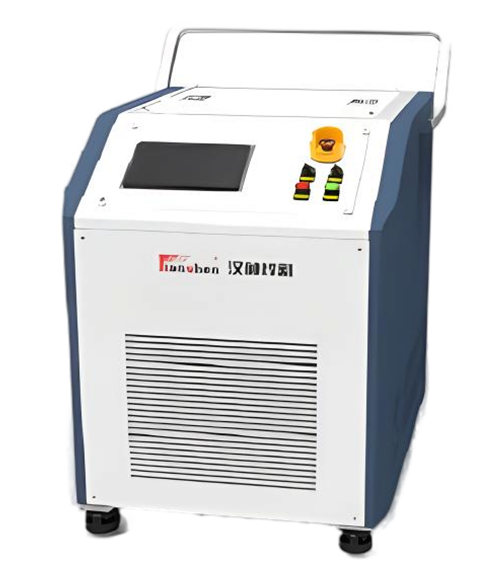
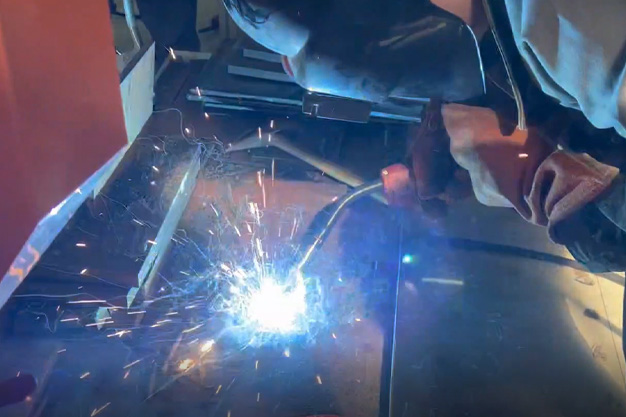
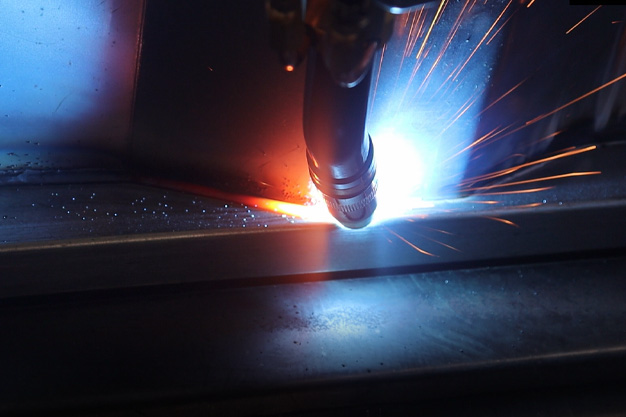
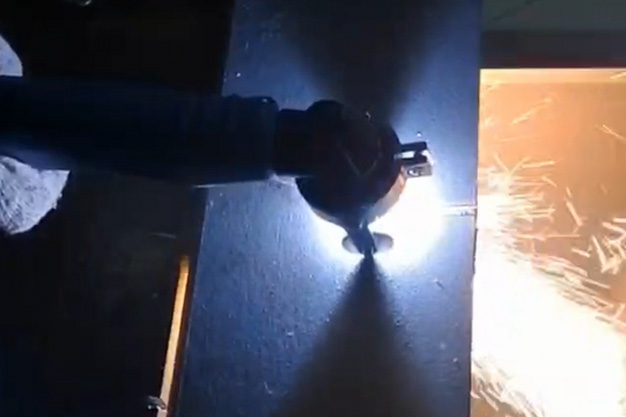
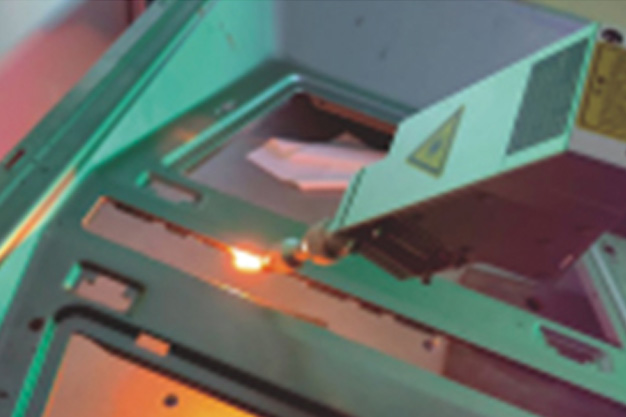
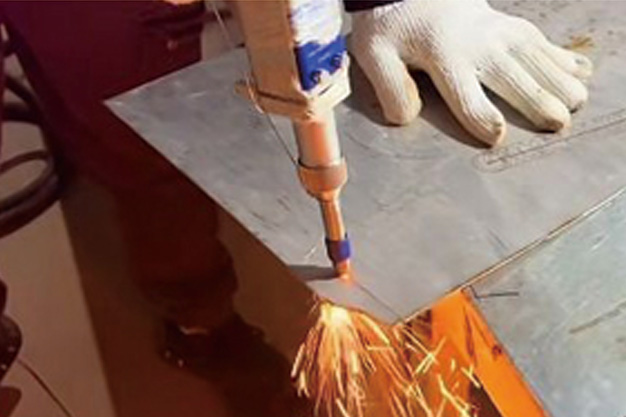
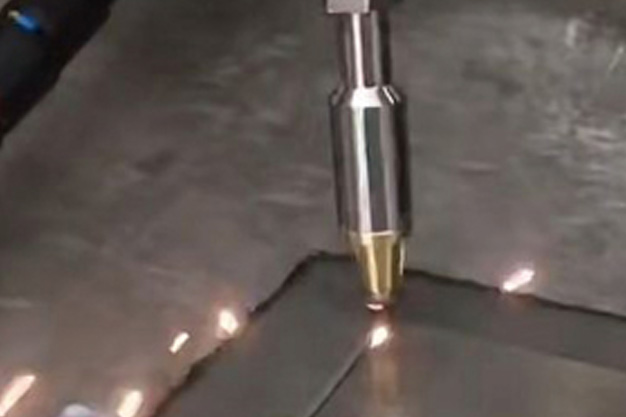
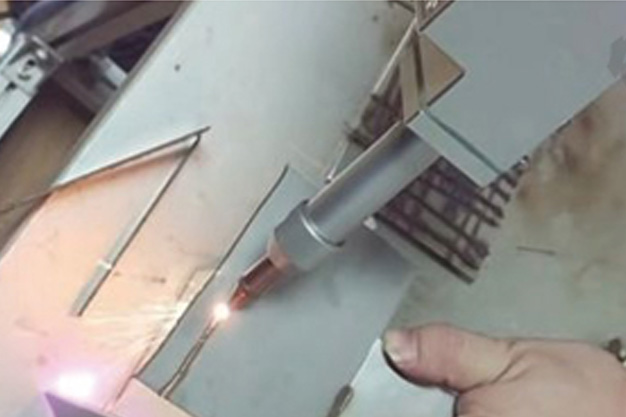
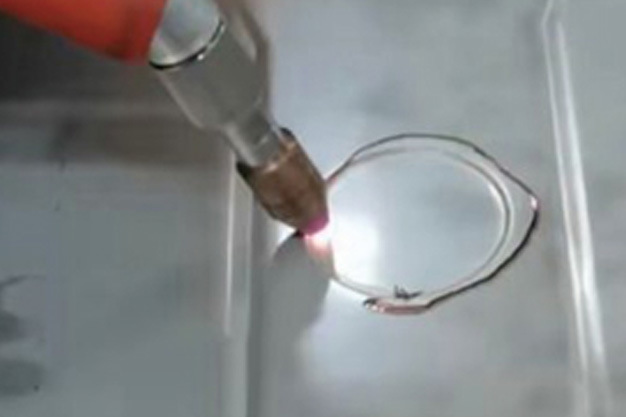
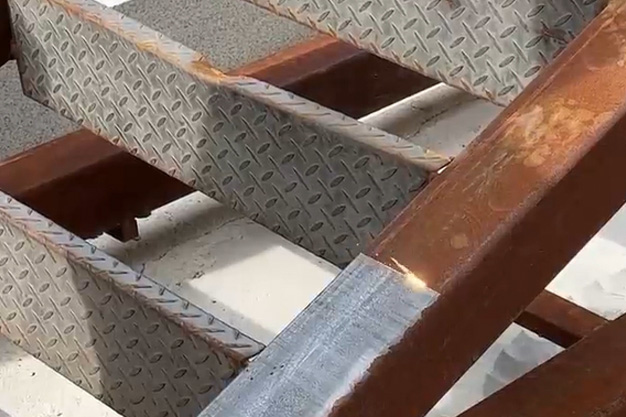
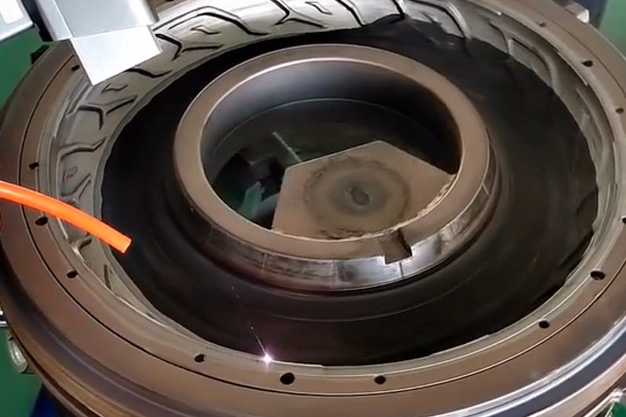























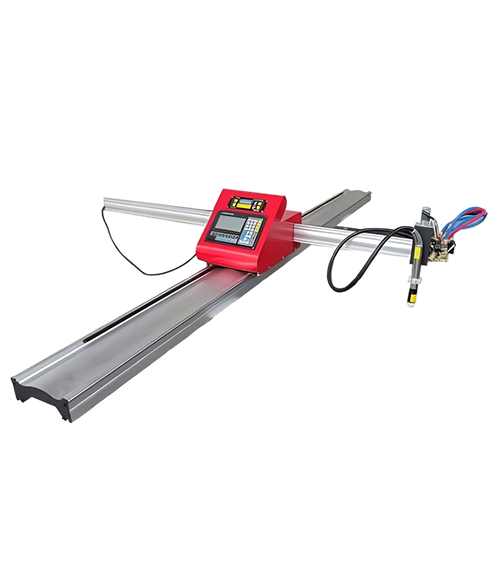





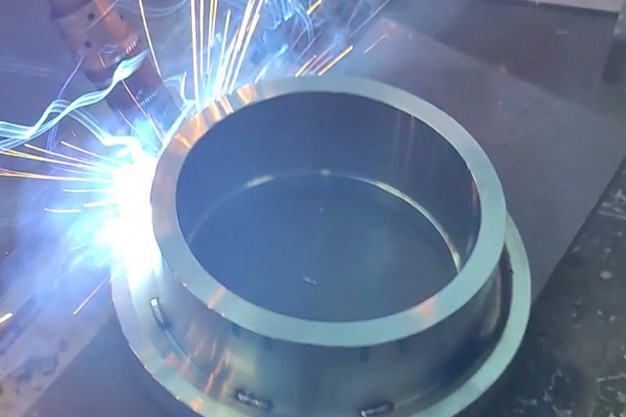












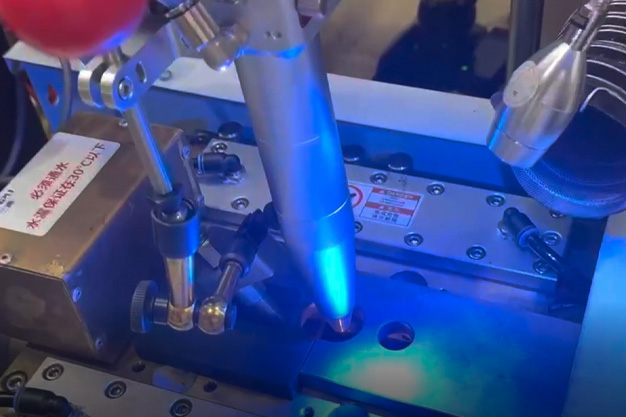
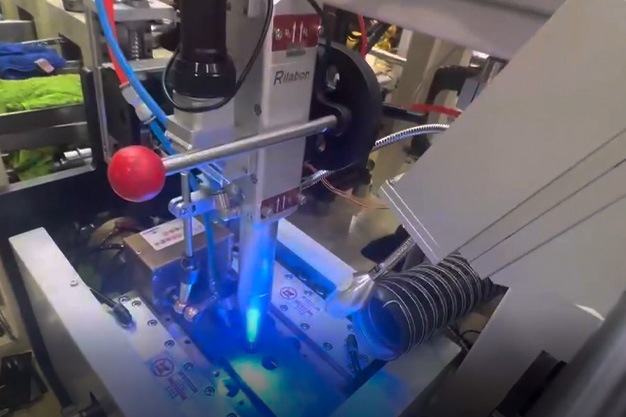


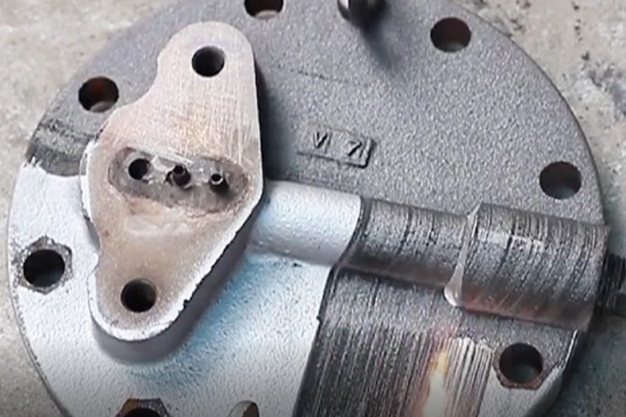
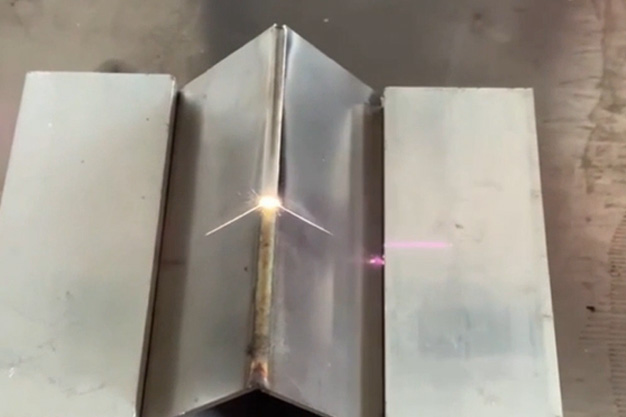




















 Wuxi HanShen
Wuxi HanShen